Cat. #152742
Chicken IgY precipitating protein Vector
Cat. #: 152742
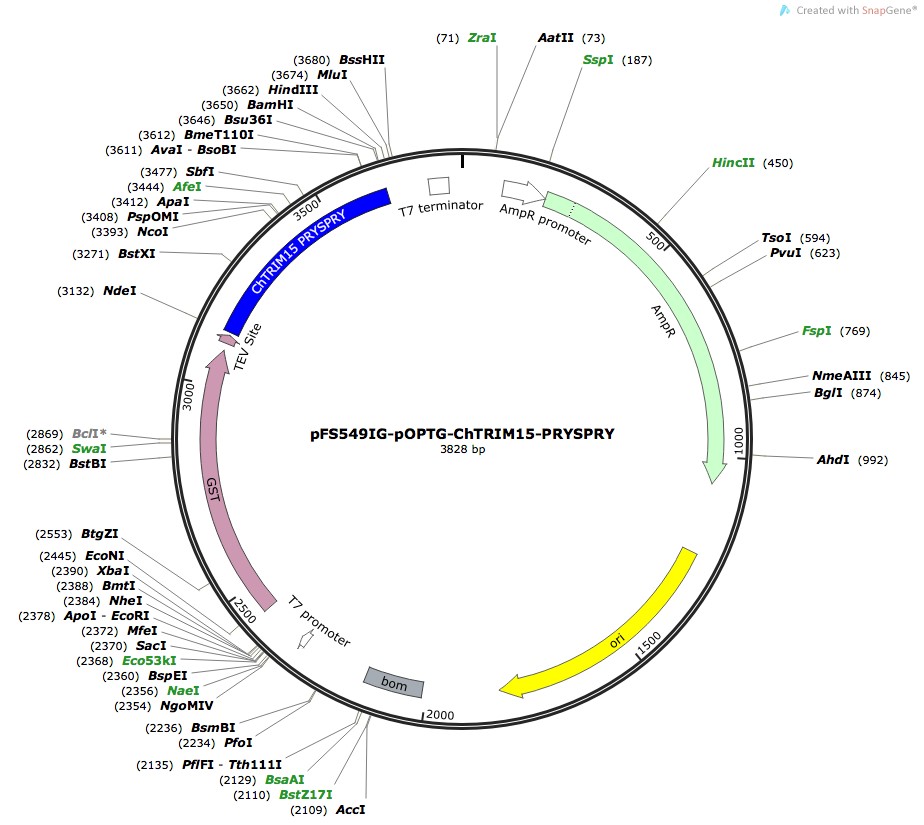
Sub-type: pFS549IG-pOPTG-ChZNF777 plasmid.
Availability: 3-5 days
Target: Chicken IgY
Bacterial Resistance: Ampicillin
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Inventor: Dr Frederic Sorgeloos
Institute: University of Cambridge
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY (for other uses, please contact the licensing team)
- Tool name: Chicken IgY precipitating protein Vector
- Research fields: Genetics
- Tool sub type: pFS549IG-pOPTG-ChZNF777 plasmid.
- Backbone size without insert: 3828
- Bacterial resistance: Ampicillin
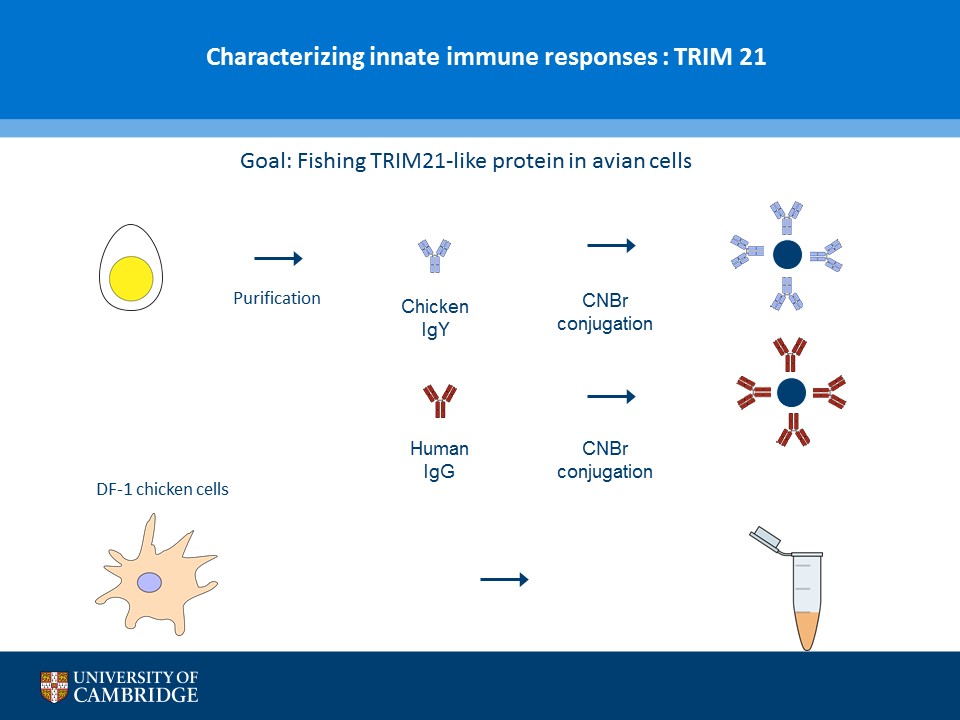
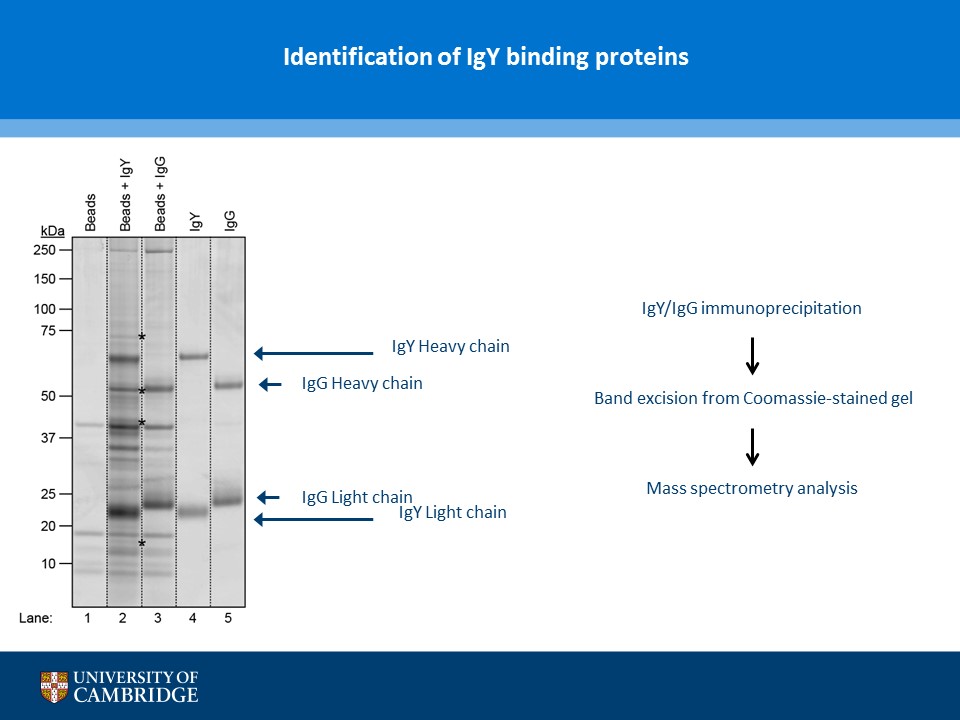
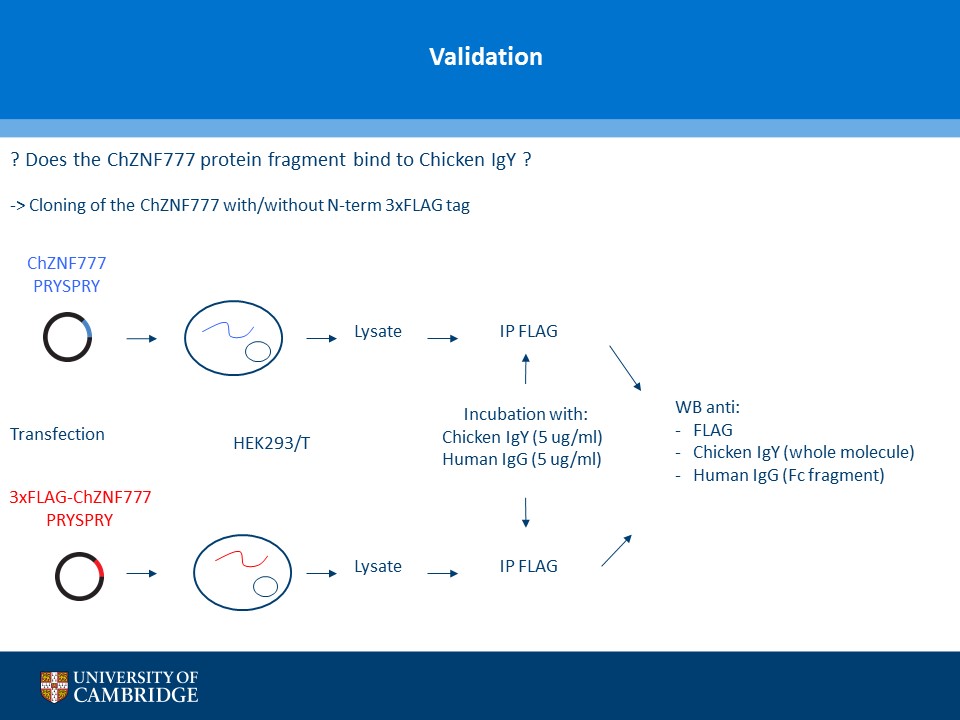
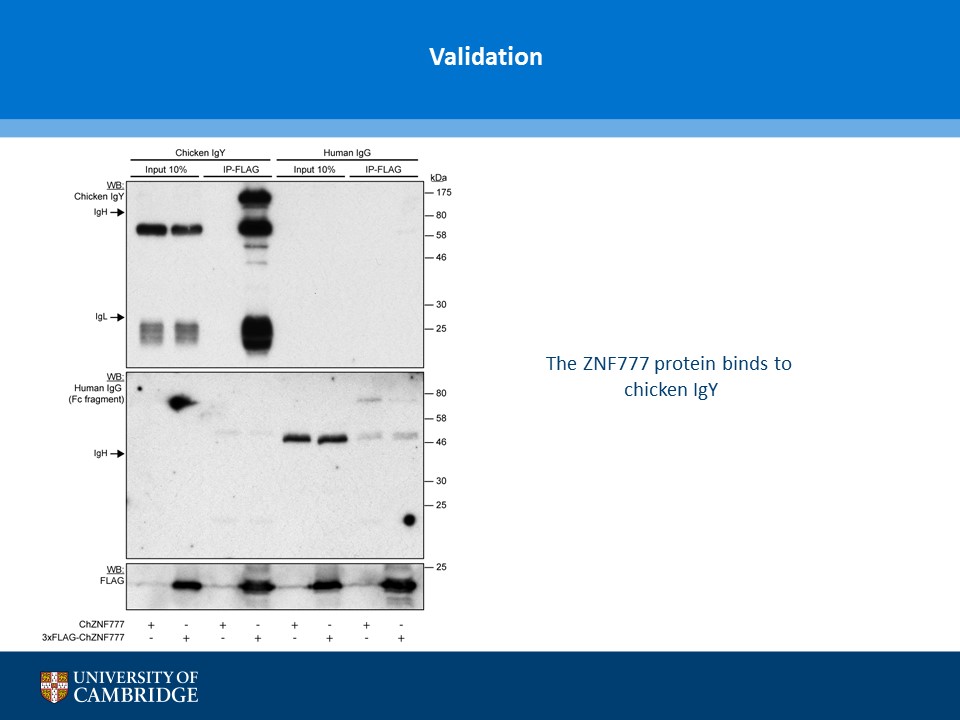
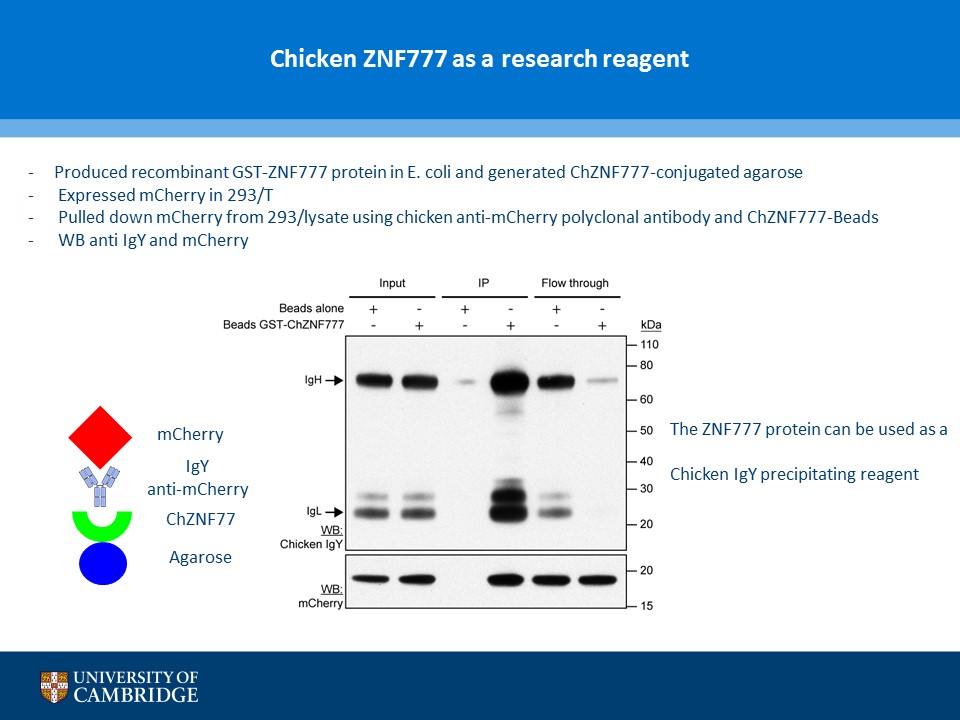
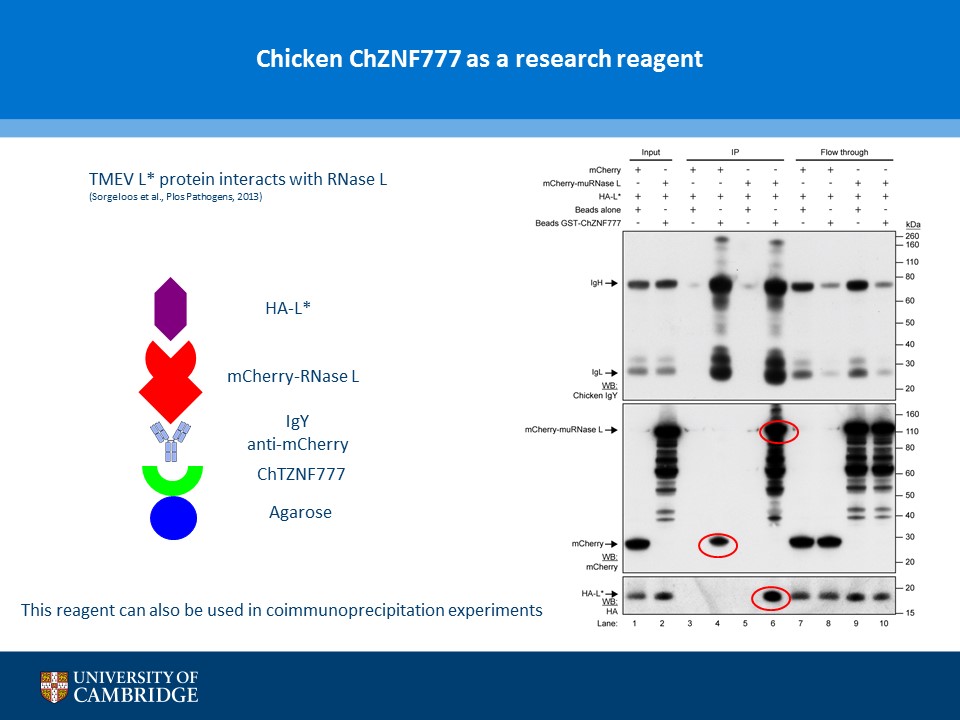
- Description: A novel chicken IgY binding protein was identified through a reverse protein capture approach using sepharose beads either conjugated to chicken IgY (whole molecule) or human IgG (Fc fragment). The conjugates were incubated with a lysate prepared from chicken DF-1 cells (Figure A). The resulting immunocomplex was washed and separated by SDS-PAGE. Protein bands were selected based on their presence in the Beads + IgY lane and absence in the control (IgY, IgG, Beads only and Beads + IgG) lanes (Figure B). The proteins were excised and analysed using Mass Spec. A domain from one of the proteins, ZNF777 (unique to the IgY pull down experiment) was further characterised through a series of co-IP experiments. The domain was expressed with or without a FLAG tag in HEK293 cells and incubated with chicken IgY or human IgG (Figure C). The immunoprecipitates and inputs were analysed by western blot using antibodies against chicken IgY, human IgG or FLAG. Figure D shows that the protein domain when FLAG tagged immunoprecipitates chicken IgY but not human IgG. Experiments without the FLAG tag failed to precipitate IgY or IgG. Subsequent experiments demonstrated that the interaction between the protein domain and IgY is direct and in the submicromolar range (590 nM). A proof of principle study (shown in Figure E) showed that the protein domain when conjugated to agarose serves to capture a chicken polyclonal antibody against mCherry by immunoprecipitation together with its own protein target. Finally these studies were extended to demonstrate that protein domain can be used in co-IP studies (Figure F).
- Additional notes: A novel chicken IgY binding protein was identified through a reverse protein capture approach using sepharose beads either conjugated to chicken IgY (whole molecule) or human IgG (Fc fragment). The conjugates were incubated with a lysate prepared from chicken DF-1 cells (Figure A). The resulting immunocomplex was washed and separated by SDS-PAGE. Protein bands were selected based on their presence in the Beads + IgY lane and absence in the control (IgY, IgG, Beads only and Beads + IgG) lanes (Figure B). The proteins were excised and analysed using Mass Spec. A domain from one of the proteins, ZNF777 (unique to the IgY pull down experiment) was further characterised through a series of co-IP experiments. The domain was expressed with or without a FLAG tag in HEK293 cells and incubated with chicken IgY or human IgG (Figure C). The immunoprecipitates and inputs were analysed by western blot using antibodies against chicken IgY, human IgG or FLAG. Figure D shows that the protein domain when FLAG tagged immunoprecipitates chicken IgY but not human IgG. Experiments without the FLAG tag failed to precipitate IgY or IgG. Subsequent experiments demonstrated that the interaction between the protein domain and IgY is direct and in the submicromolar range (590 nM). A proof of principle study (shown in Figure E) showed that the protein domain when conjugated to agarose serves to capture a chicken polyclonal antibody against mCherry by immunoprecipitation together with its own protein target. Finally these studies were extended to demonstrate that protein domain can be used in co-IP studies (Figure F).
- Recommended controls: Chicken IgY
Target Details
- Target: Chicken IgY