Cat. #153323
Anti-CEACAM8 (CD66b) [6/40c]
Cat. #: 153323
Sub-type: Primary antibody
Unit size: 100 ug
Availability: 3-4 weeks
Target: CEACAM8, CD66b; CD67
Class: Monoclonal
Application: ELISA ; FACS ; IHC ; IP ; WB
Reactivity: Human
Host: Mouse
£300.00
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Inventor: Bernhard B. Singer
Institute: LeukoCom
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY (for other uses, please contact the licensing team)
- Name: Anti-CEACAM8 (CD66b) [6/40c]
- Alternate name: CD66b; CD67
- Cancer type filter: Colorectal cancer
- Cancers detailed: Broadly Applicable;Intestinal
- Research fields: Immunology
- Clone: 6/40c
- Tool sub type: Primary antibody
- Class: Monoclonal
- Conjugation: Unconjugated
- Molecular weight: 100 kDa
- Strain: Balb/c
- Reactivity: Human
- Host: Mouse
- Application: ELISA ; FACS ; IHC ; IP ; WB
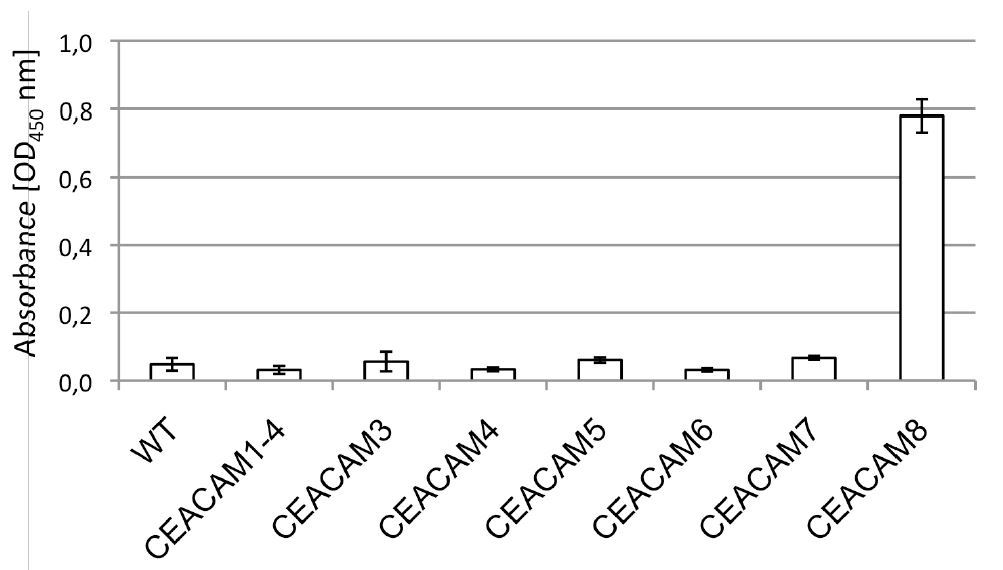
- Description: Monoclonal antibody directed against CEACAM8, used to investigate cell signalling-mediated effects on immune responses, including in cancer cells. Background and Research Application The carcino-embryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8 (CEACAM8) is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked protein also known as CD67, CGM6, and NCA-95. CEACAM8 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)-like subfamily. CEACAM8, expressed on granulocytes, has been reported to induce activation in neutrophils and to be involved in heterophilic adhesion with CEACAM6. It is not expressed by peripheral blood monocytes or lymphocytes. CEACAM8 is stored in specific vesicles of granulocytes and acts as a marker for specific vesicles for exocytosis. The soluble form of CEACAM8 binds to CEACAM1, a trans-membrane-bound molecule expressed by certain normal epithelial, endothelial, different leukocyte subpopulations and some cancer cells.
- Immunogen: Recombinant soluble human CEACAM8-Fc produced in HEK293 cells
- Immunogen uniprot id: P31997
- Isotype: IgG1 kappa
- Myeloma used: P3/NS1/1-Ag4.1
Target Details
- Target: CEACAM8, CD66b; CD67
- Molecular weight: 100 kDa
- Target background: Monoclonal antibody directed against CEACAM8, used to investigate cell signalling-mediated effects on immune responses, including in cancer cells. Background and Research Application The carcino-embryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8 (CEACAM8) is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked protein also known as CD67, CGM6, and NCA-95. CEACAM8 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)-like subfamily. CEACAM8, expressed on granulocytes, has been reported to induce activation in neutrophils and to be involved in heterophilic adhesion with CEACAM6. It is not expressed by peripheral blood monocytes or lymphocytes. CEACAM8 is stored in specific vesicles of granulocytes and acts as a marker for specific vesicles for exocytosis. The soluble form of CEACAM8 binds to CEACAM1, a trans-membrane-bound molecule expressed by certain normal epithelial, endothelial, different leukocyte subpopulations and some cancer cells.
Applications
- Application: ELISA ; FACS ; IHC ; IP ; WB
Handling
- Format: Liquid
- Concentration: 1 mg/ml
- Unit size: 100 ug
- Storage buffer: PBS with 0.02% azide
- Storage conditions: Store at -20° C frozen. Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles
- Shipping conditions: Dry ice
References
- Singer et al. 2014. PLoS One. 9(4):e94106. PMID: 24743304.
- Soluble CEACAM8 interacts with CEACAM1 inhibiting TLR2-triggered immune responses.
- Klaile et al. 2013. Respir Res. 14:85. PMID: 23941132.
- Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)-related cell adhesion molecules are co-expressed in the human lung and their expression can be modulated in bronchial epithelial cells by non-typable Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, TLR3, and type I and II int