Cat. #152053
pKH2 Beta-Synuclein P123H Vector
Cat. #: 152053
Availability: Please enquire for quantities and pricing
Target: Beta-synuclein
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Inventor: Dr Fiona Benson
Institute: Lancaster University
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY (for other uses, please contact the licensing team)
- Tool name: pKH2 Beta-Synuclein P123H Vector
- Research fields: Neurobiology
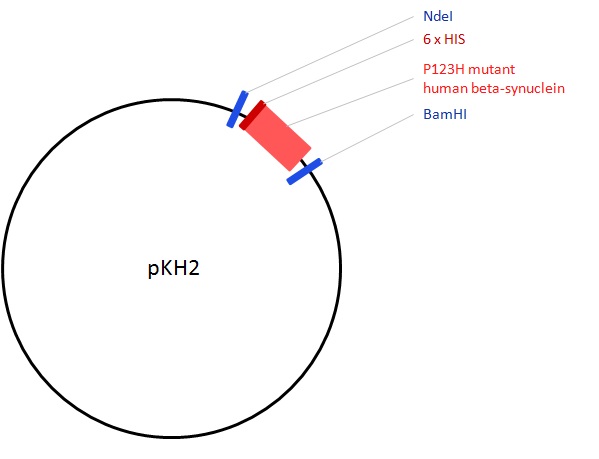
- Description: pKH2 ("P123H") is a derivative of pET15b with the open reading frame encoding the P123H mutant human beta-synuclein (ÄÂĂÂ-synuclein) cloned in via the vector NdeI and BamHI restriction sites. It was constructed via site-specific mutagenesis of pJEK12 (pET15b-wt ÄÂĂÂ-synuclein), replacing the C at position 368 in the ORF nucleotide sequence with A, thus altering the 123rd codon from CCC encoding proline (P) to CAC encoding histidine (H). In this construct P123H ÄÂĂÂ-synuclein is expressed as a fusion protein with an N-terminal six His tag.
- Additional notes: Beta synuclein is an abundant pre-synaptic phosphoprotein that is found in the brain and is homolgous to alpha-synuclein. Beta-synuclein is distinct from alha-synuclein in that it lacks the majority of the hydrophobic non-amyloid-beta component of the Alzeheimer's disease amyloid region. Due to this beta-synuclein is less likely to form insoluble aggregates when compared to alpha-synuclein. It is thought that beta-synuclein may have a protective role against alpha-synucleinopathies. Overexpression of beta-synuclein mutants (P123H and V70M) in neuroblastoma cells results in enhanced lysosomal pathology suggesting a causative role for these missense mutations in neurodegeneration stimulation
Target Details
- Target: Beta-synuclein
Application Details
- Application notes: pKH2 ("P123H") is a derivative of pET15b with the open reading frame encoding the P123H mutant human beta-synuclein (β-synuclein) cloned in via the vector NdeI and BamHI restriction sites. It was constructed via site-specific mutagenesis of pJEK12 (pET15b-wt β-synuclein), replacing the C at position 368 in the ORF nucleotide sequence with A, thus altering the 123rd codon from CCC encoding proline (P) to CAC encoding histidine (H). In this construct P123H β-synuclein is expressed as a fusion protein with an N-terminal six His tag.