Cat. #151713
GFP-KSC4 Keratinocyte Stem Cell Line
Cat. #: 151713
Unit size: 1x10^6 cells / vial
Availability: 10-12 weeks
Organism: Mouse
Disease: Dermatology
Model: Transgenic
£575.00
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Inventor: Julia Reichelt
Institute: Newcastle University
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY (for other uses, please contact the licensing team)
- Name: GFP-KSC4 Keratinocyte Stem Cell Line
- Research fields: Drug development;Stem cell biology
- Organism: Mouse
- Disease: Dermatology
- Growth properties: Adherent
- Model: Transgenic
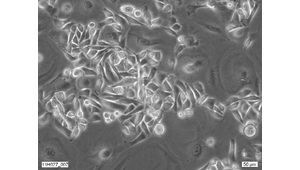
- Description: The GFP-KSC4 Keratinocyte Stem Cell line can be used for the generation of in vitro epidermal ‘skin equivalents’ to be used as screening tools to look at the activity of NCE’s and/or NBE’s of dermatological interest, and/or to screen for such NCE and/or NBE in high throughput systems. It may also be of use to non-pharmaceutical healthcare and/or cosmetic companies involved in the personal vitality and/or beauty product development segments. Murine keratinocyte stem cell line.
- Production details: Keratinocytes were isolated from neonatal homozygous C57BL/6-Tg(CAG-EGFP)1Osb/J mouse skin. The cell line was established by growing cells for the first 8 passages in co-culture with 3T3-J2 fibroblast feeder cells. From passage 9 onwards cells were grown without feeder cells.
- Cellosaurus id: CVCL_W142
Target Details
- Target: GFP-KSC4
Handling
- Format: Frozen
- Growth medium: See remarks...
- Unit size: 1x10^6 cells / vial
- Shipping conditions: Dry ice
References
- Reichelt and Haase. 2010. Methods Mol Biol 585:59-69
- PMID: 19907996 Okabe et al. 1997 FEBS Letters 407:313-9. PMID: 9175875 HÄ?her T et al., 2011. Stem Cell Rev. PMID: 21874280 Vollmers A et al., 2011. PMID: 21892602