Cat. #160834
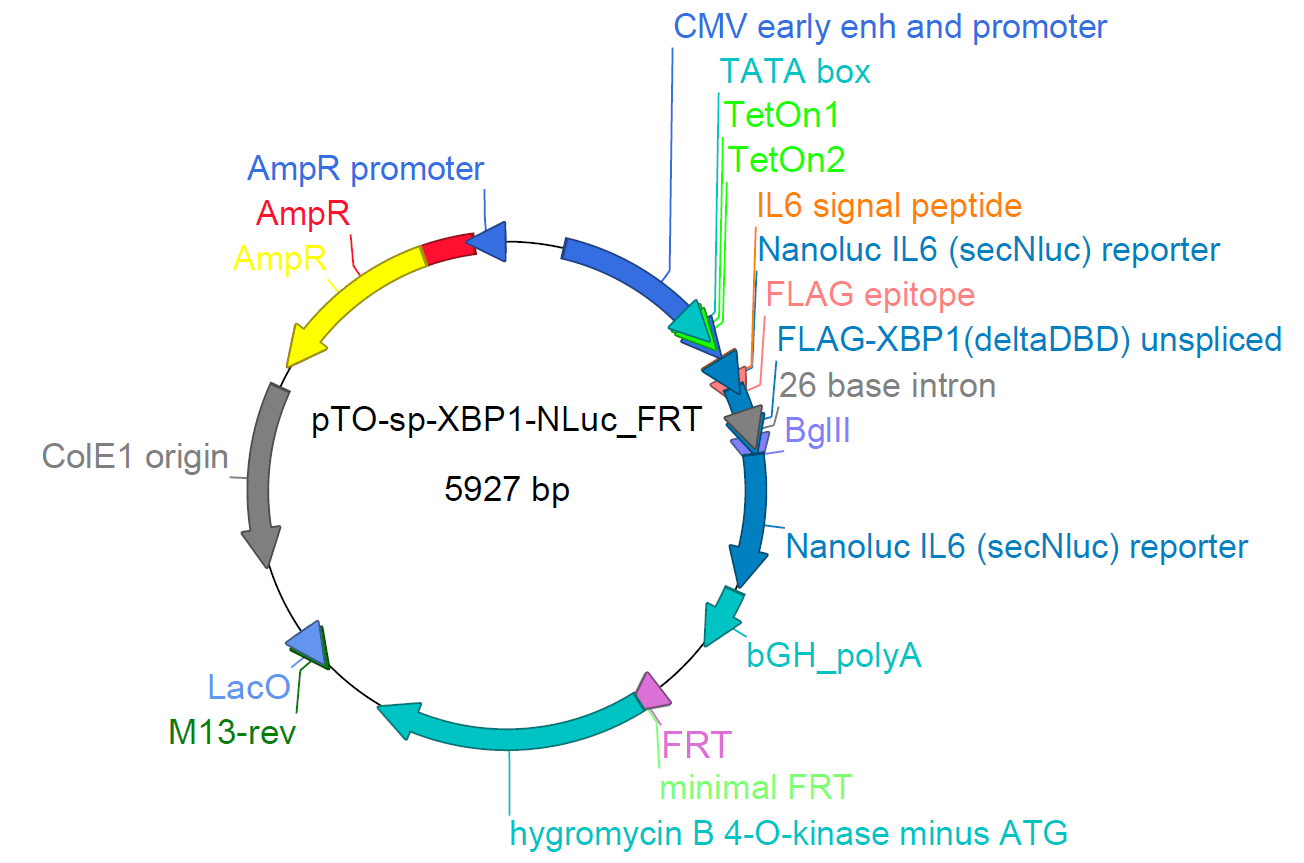
pTO-sp-XBP1-NLuc-FRT XBP1 splicing reporter plasmid
Cat. #: 160834
Sub-type: pTO-HA-Strep-GW-FRT backbone for creation of stable cell line using Flp-In HEK-293 T-Rex cells
Availability: Please enquire for quantities and pricing
Target: activation of IRE1 branch of unfolded protein response
Bacterial Resistance: Ampicillin
Selectable Markers: Hygromycin
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Inventor: Tina Sket ; Andrii Domanskyi
Institute: University Of Helsinki
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY (for other uses, please contact the licensing team)
- Tool name: pTO-sp-XBP1-NLuc-FRT XBP1 splicing reporter plasmid
- Alternate name: XBP1-NLuc reporter
- Research fields: Cancer;Neurobiology
- Tool sub type: pTO-HA-Strep-GW-FRT backbone for creation of stable cell line using Flp-In HEK-293 T-Rex cells
- Backbone size without insert: 5051 bp
- Bacterial resistance: Ampicillin
- Selectable markers: Hygromycin
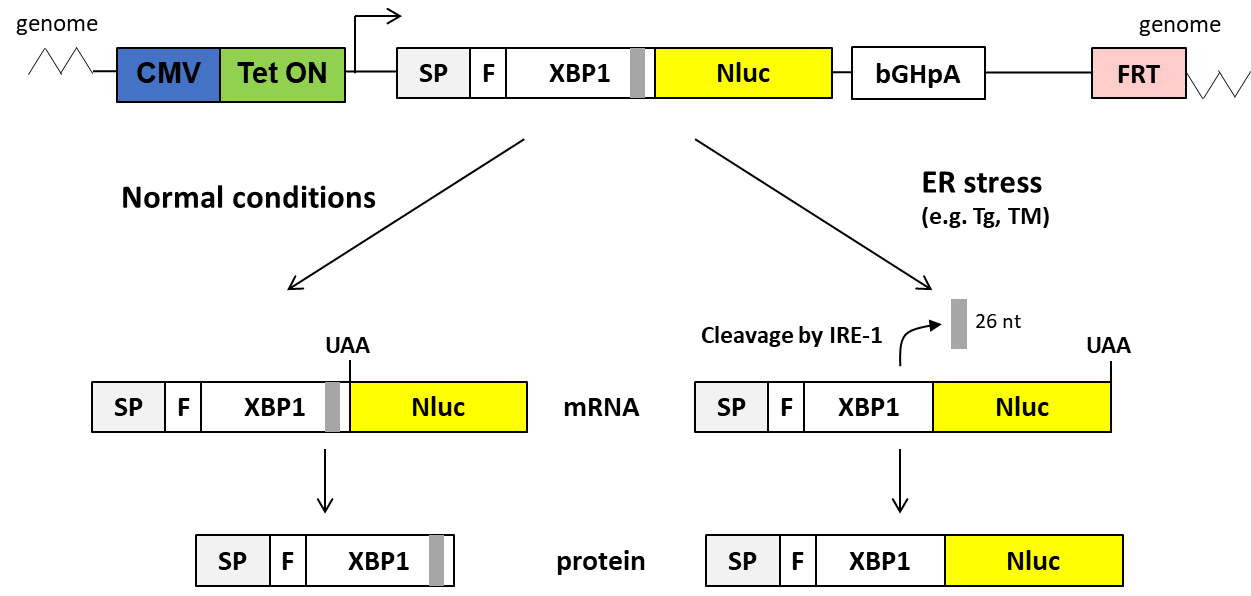
- Description: secNLuc-XBP1 fragment (876 bp) can be subcloned by using HindIII and ApaI restriction sites The plasmid can be used in transient transfections to cells, which do not express Tet repressor protein
- Additional notes: Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is caused by the accumulation of unfolded proteins in the ER, which leads to the activation of unfolded protein response (UPR) through three transmembrane protein sensors located in the ER membrane. The sensors correspond to three branches of the UPR, namely protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK), activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6), and inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1) branches. Upon ER stress, IRE1 dimerizes and oligomerizes, and its endonuclease domain is activated. It specifically targets X-box-binding protein 1 (XBP1) mRNA, from which a 26 nt intron is spliced. This allows a complete translation of spliced XBP1 mRNA into a functional protein that acts as a transcription factor. Together with the other pathways, the UPR leads to a decrease in the protein folding load by causing a reduction in the general level of protein translation, and by inducing the expression of protein folding machinery. However, if the UPR is activated continuously for a long time, the apoptotic pathway will be triggered, and the cell will die. The plasmid is composed of a backbone with ampicillin resistance gene that allows selection of transformed bacterial clones, origin of replication site for bacterial amplification, CMV promoter for high expression of reporter construct with secNLuc-XBP1 fragment for XBP1-spliced dependent transcription of secreted luciferase reporter, tetracycline inducible element for regulated expression of target gene, FRT recombination site for recombination during transfection and hygromycin resistance gene for selection of mammalian clones with successful genomic integration of target construct to Flp-In HEK-293 T-Rex cells
- Recommended controls: pTO-sp-NLuc_FRT - an identical plasmid, apart from XBP1 fragment (NLuc was retained); results in constitutive expression of reporter protein independently of XBP1 splicing
Target Details
- Target: activation of IRE1 branch of unfolded protein response
Application Details
- Application notes: secNLuc-XBP1 fragment (876 bp) can be subcloned by using HindIII and ApaI restriction sites The plasmid can be used in transient transfections to cells, which do not express Tet repressor protein
Related Tools
- Related tools: XBP1 splicing reporter (XSARA) cell line