Cat. #160866
Anti-PAX-FOXO1 [PaxF]
Cat. #: 160866
Sub-type: Primary antibody
Unit size: 100 ug
Availability: 3-4 weeks
Target: The junction region of the PAX3-FOXO1 and the PAX7-FOXO1 fusion proteins
Class: Monoclonal
Application: ChIP ; IHC ; IF ; IP ; WB ; ChIP-seq
Reactivity: Human
Host: Mouse
£300.00
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Institute: National Human Genome Research Institute
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY (for other uses, please contact the licensing team)
- Name: Anti-PAX-FOXO1 [PaxF]
- Alternate name: PFM.2
- Research fields: Cancer
- Clone: PaxF
- Tool sub type: Primary antibody
- Class: Monoclonal
- Molecular weight: 105 kDa
- Strain: Balb/c
- Reactivity: Human
- Host: Mouse
- Application: ChIP ; IHC ; IF ; IP ; WB ; ChIP-seq
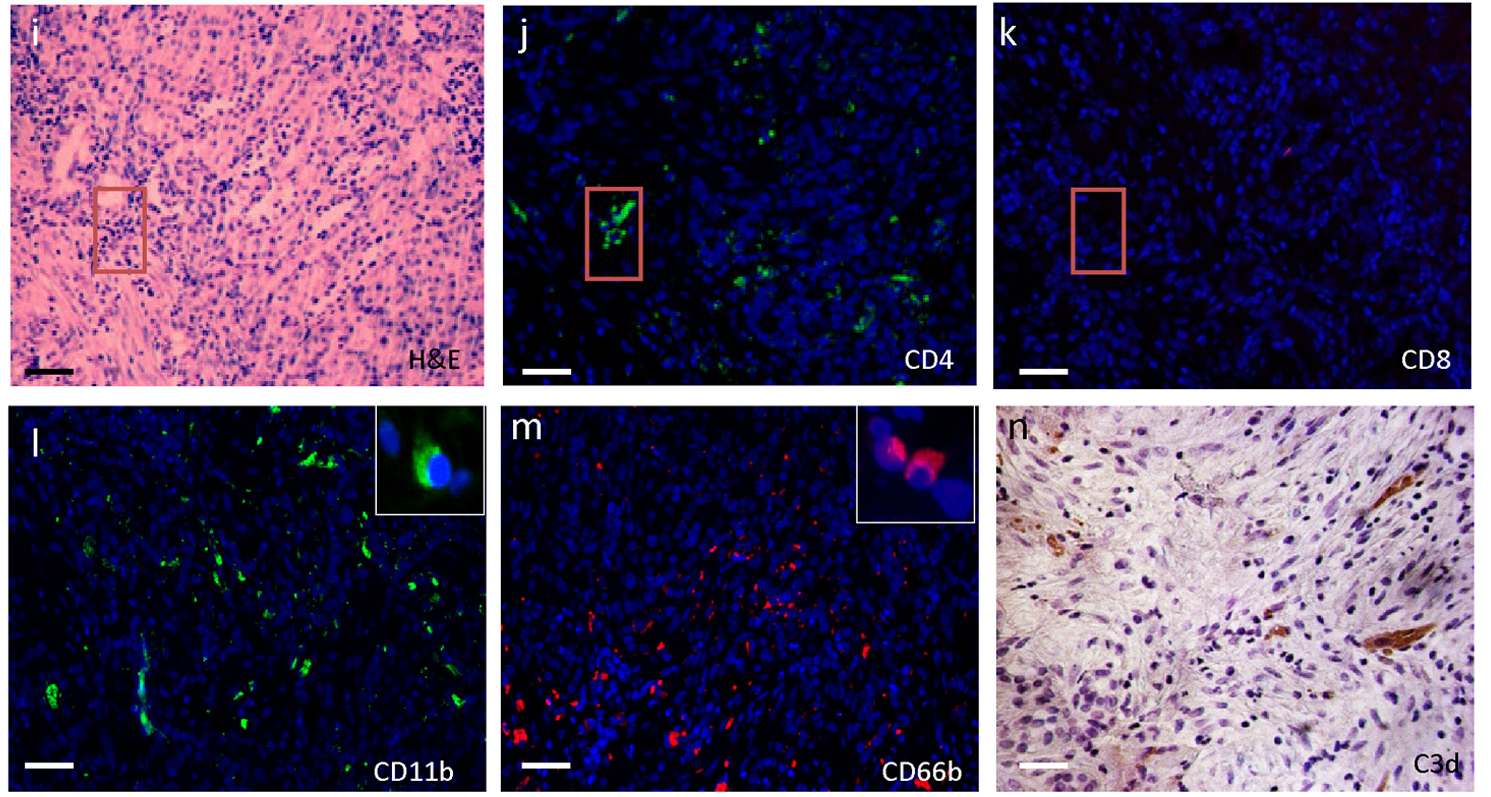
- Description: Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma (ARMS) is an aggressive pediatric cancer and cases with fusion oncoproteins PAX7-FOXO1 and PAX3-FOXO1 have a poor prognosis. Determination of the fusion status is important for RMS diagnostics and therapies. This antibody is specific for the PAX3-FOXO1 and PAX7-FOXO1 and therefore is a valuable tool to study the oncogenesis of ARMS
- Immunogen: LH conjugated with peptide PF corresponding to the PAX3-FOXO1 translocation region aa 100-117 (TIGNGLSPQNSIRHNLSL) in Freund’s adjuvant.
- Isotype: IgG2b kappa
- Myeloma used: P3X63Ag8.653
- Recommended controls: Cell lysate from FP-RMS lines (e.g., RH-4, RH-28, RH-30, RMS-13)
Target Details
- Target: The junction region of the PAX3-FOXO1 and the PAX7-FOXO1 fusion proteins
- Molecular weight: 105 kDa
Applications
- Application: ChIP ; IHC ; IF ; IP ; WB ; ChIP-seq
Handling
- Concentration: 1 mg/mL
- Unit size: 100 ug
- Storage buffer: PBS with 0.02% azide
- Storage conditions: Product stable at -20°C when stored undiluted. Store aliquoted, avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
- Shipping conditions: Dry ice
References
- Azorsa et al. 2021. Mod Pathol. 34(4):748-757. PMID: 33299109.
- Gryder et al. 2017. Cancer Discov. 7(8):884-899. PMID: 28446439.
- Cao et al. 2010. Cancer Res. 70(16):6497-508. PMID: 20663909.
- Khan et al. 1999. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 96(23):13264-9. PMID: 10557309.


![Anti-CAR Whitlow Linker [1C3C3]](https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-6-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025-300x322.jpg 300w, https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-6-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025-280x300.jpg 280w, https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-6-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025-954x1024.jpg 954w, https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-6-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025-768x824.jpg 768w, https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-6-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025.jpg 1193w)