Cat. #153817
CMV4pFlagSiR TDP43 F4L Vector
Cat. #: 153817
Sub-type: pFLAG-CMV4
Availability: Please enquire for quantities and pricing
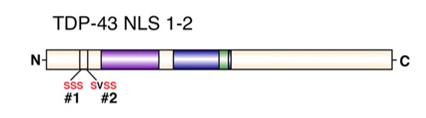
Target: Mutant TDP43 not able to bind RNA
Bacterial Resistance: Ampicillin
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Inventor: Prof Emanuele Buratti
Institute: International Centre For Genetic Engineering And Biotechnology (ICGEB)
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY (for other uses, please contact the licensing team)
- Tool name: CMV4pFlagSiR TDP43 F4L Vector
- Alternate name: TARDBP, TAR DNA Binding Protein, TDP-43, TAR DNA-Binding Protein 43, ALS10
- Research fields: Genetics;Neurobiology;Microbiology
- Tool sub type: pFLAG-CMV4
- Backbone size without insert: 6271
- Bacterial resistance: Ampicillin
- Description: Concentration 1.2mg/ml
- Additional notes: The TAR DNA-binding protein (TDP-43) is a highly conserved heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) that controls the transcription, splicing and RNA stability of specific genes. The protein associates with single-stranded RNA and DNA sequences, and exhibits remarkable specificity for UG/TG dinucleotide repeats. Regulation of the human low-molecular-weight neurofilament (hNFL) by TDP-43 has also been reported to occur through 3′ UTR recruitment. TDP-43 is the major protein in inclusions from patients suffering from frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) with ubiquitin-positive inclusions and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The TAR DNA-binding protein (TDP-43) is a highly conserved heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) that controls the transcription, splicing and RNA stability of specific genes. The protein associates with single-stranded RNA and DNA sequences, and exhibits remarkable specificity for UG/TG dinucleotide repeats. Regulation of the human low-molecular-weight neurofilament (hNFL) by TDP-43 has also been reported to occur through 3′ UTR recruitment. TDP-43 is the major protein in inclusions from patients suffering from frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) with ubiquitin-positive inclusions and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Target Details
- Target: Mutant TDP43 not able to bind RNA
Application Details
- Application notes: Concentration 1.2mg/ml
References
- Ayala et al. 2008. J Cell Sci. 121(Pt 22):3778-85. PMID: 18957508.
- Structural determinants of the cellular localization and shuttling of TDP-43.