Cat. #153782
Anti-ERCC1 [8F1]
Cat. #: 153782
Sub-type: Primary antibody
Unit size: 100 ug
Availability: 3-4 weeks
Target: ERCC1
Class: Monoclonal
Application: FACS ; IHC ; IF ; IP ; WB
Reactivity: Human ; Rat
Host: Mouse
£300.00
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Inventor: Rick Wood
Institute: Cancer Research UK, London Research Institute: Lincoln's Inn Fields
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY (for other uses, please contact the licensing team)
- Name: Anti-ERCC1 [8F1]
- Alternate name: ERCC Excision Repair 1, Endonuclease Non-Catalytic Subunit, Excision Repair Cross-Complementing Rodent Repair Deficiency, Complementation Group 1 (Includes Overlapping Antisense Sequence), Excision Repair Cross-Complementation Group 1, DNA Excision Repair Protein ERCC-1, COFS4, RAD1, UV2
- Research fields: Cancer;Genetics
- Tool sub type: Primary antibody
- Class: Monoclonal
- Conjugation: Unconjugated
- Molecular weight: 36 kDa
- Strain: Balb/c
- Reactivity: Human ; Rat
- Host: Mouse
- Application: FACS ; IHC ; IF ; IP ; WB
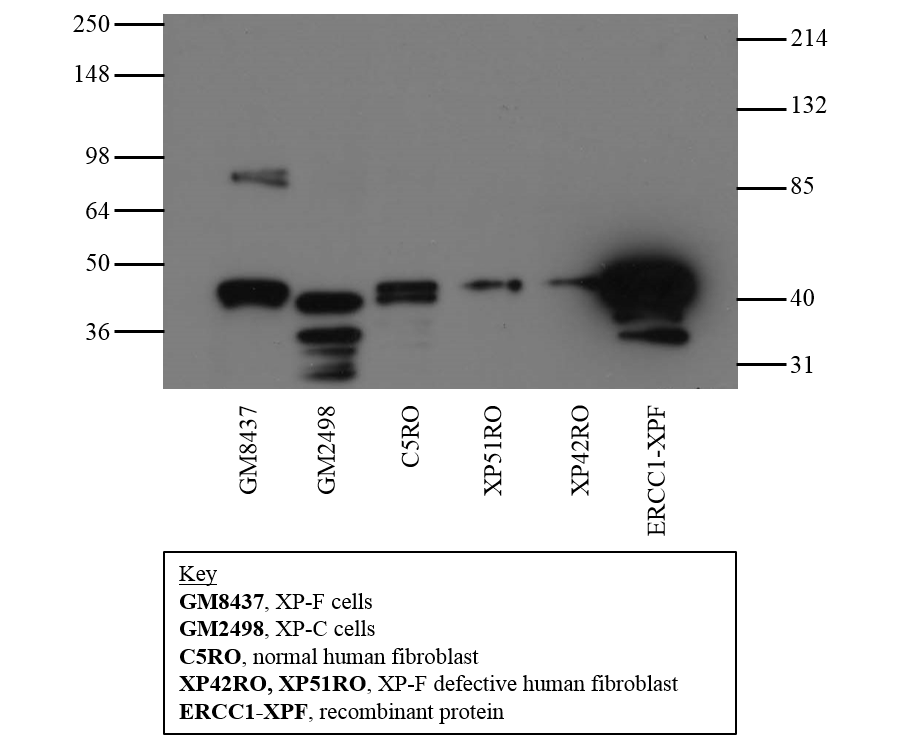
- Description: The mammalian ERCC1 (Excision Repair Cross Complementing) polypeptide is required for nucleotide excision repair (NER) of damaged DNA and is homologous to Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD10, which functions in repair and mitotic intrachromosomal recombination. NER mechanism involves dual incisions on both sides of the damage catalyzed by two nucleases. In mammalian cells XPG cleaves 3' of the DNA lesion while the ERCC1-XPF complex makes the 5' incision. Elevated levels of ERCC1 have been reported in Cisplatin-resistant cells. Defects in ERCC1 are the cause of cerebro-oculo-facio-skeletal syndrome type 4 (COFS4) [MIM:610758]. COFS is a degenerative autosomal recessive disorder of prenatal onset affecting the brain, eye and spinal cord. After birth, it leads to brain atrophy, hypoplasia of the corpus callosum, hypotonia, cataracts, microcornea, optic atrophy, progressive joint contractures and growth failure. Facial dysmorphism is a constant feature. Abnormalities of the skull, eyes, limbs, heart and kidney also occur.
- Immunogen: Full length, HIS-tagged recombinant Human ERCC1
- Isotype: IgG2b
- Recommended controls: Tonsil
Target Details
- Target: ERCC1
- Molecular weight: 36 kDa
- Tissue cell line specificity: Tonsil
- Target background: The mammalian ERCC1 (Excision Repair Cross Complementing) polypeptide is required for nucleotide excision repair (NER) of damaged DNA and is homologous to Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD10, which functions in repair and mitotic intrachromosomal recombination. NER mechanism involves dual incisions on both sides of the damage catalyzed by two nucleases. In mammalian cells XPG cleaves 3' of the DNA lesion while the ERCC1-XPF complex makes the 5' incision. Elevated levels of ERCC1 have been reported in Cisplatin-resistant cells. Defects in ERCC1 are the cause of cerebro-oculo-facio-skeletal syndrome type 4 (COFS4) [MIM:610758]. COFS is a degenerative autosomal recessive disorder of prenatal onset affecting the brain, eye and spinal cord. After birth, it leads to brain atrophy, hypoplasia of the corpus callosum, hypotonia, cataracts, microcornea, optic atrophy, progressive joint contractures and growth failure. Facial dysmorphism is a constant feature. Abnormalities of the skull, eyes, limbs, heart and kidney also occur.
Applications
- Application: FACS ; IHC ; IF ; IP ; WB
Handling
- Format: Liquid
- Concentration: 0.9-1.1 mg/ml
- Unit size: 100 ug
- Storage buffer: PBS with 0.02% azide
- Storage conditions: -20° C
- Shipping conditions: Shipping at 4° C
References
- Kuhlmann et al. 2014. Clin Chem. 60(10):1282-9. PMID: 25015375.
- ERCC1-positive circulating tumor cells in the blood of ovarian cancer patients as a predictive biomarker for platinum resistance.
- Wilcox et al. 2006. N Engl J Med. 355(24):2590
- author reply 2591. PMID: 17171818.
- DNA repair by ERCC1 in non-small-cell lung cancer.
- Reed et al. 2006. N Engl J Med. 355(10):1054-5. PMID: 16957152.
- ERCC1 measurements in clinical oncology.
- Wachters et al. 2005. Lung Cancer. 50(2):211-9. PMID: 16169122.
- ERCC1, hRad51, and BRCA1 protein expression in relation to tumour response and survival of stage III/IV NSCLC patients treated with chemotherapy.