Cat. #152117
Anti-Cytochrome P450 7B1 [M17-P3F2]
Cat. #: 152117
Sub-type: Primary antibody
Unit size: 100 ug
Availability: 3-4 weeks
Target: Cytochrome P450, family 7, subfamily B, polypeptide 1 (CYP7B1)
Class: Monoclonal
Application: ELISA ; IHC ; WB
Reactivity: Human
Host: Mouse
£300.00
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Inventor: Ayham Alnabulsi
Institute: Vertebrate Antibodies Limited
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY (for other uses, please contact the licensing team)
- Name: Anti-Cytochrome P450 7B1 [M17-P3F2]
- Research fields: Cancer;Cell signaling and signal transduction;Metabolism;Neurobiology;Tissue-specific biology
- Clone: M17-P3F2
- Tool sub type: Primary antibody
- Class: Monoclonal
- Conjugation: Unconjugated
- Strain: Balb/c
- Reactivity: Human
- Host: Mouse
- Application: ELISA ; IHC ; WB
- Description: Defects in CYP7B1 are the cause of spastic paraplegia autosomal recessive type 5A (SPG5A) [MIM:270800]. Spastic paraplegia is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a slow, gradual, progressive weakness and spasticity of the lower limbs. Rate of progression and the severity of symptoms are quite variable. Initial symptoms may include difficulty with balance, weakness and stiffness in the legs, muscle spasms, and dragging the toes when walking. In some forms of the disorder, bladder symptoms (such as incontinence) may appear, or the weakness and stiffness may spread to other parts of the body. Defects in CYP7B1 are the cause of congenital bile acid synthesis defect type 3 (CBAS3) [MIM:613812]. Clinical features include severe cholestasis, cirrhosis and liver synthetic failure. Hepatic microsomal oxysterol 7-alpha-hydroxylase activity is undetectable.
- Immunogen: Ovalbumin-conjugated synthetic peptide IQYPDSDVL (C-terminal sequence)
- Isotype: IgG1 lambda
- Myeloma used: P3X63Ag8.653
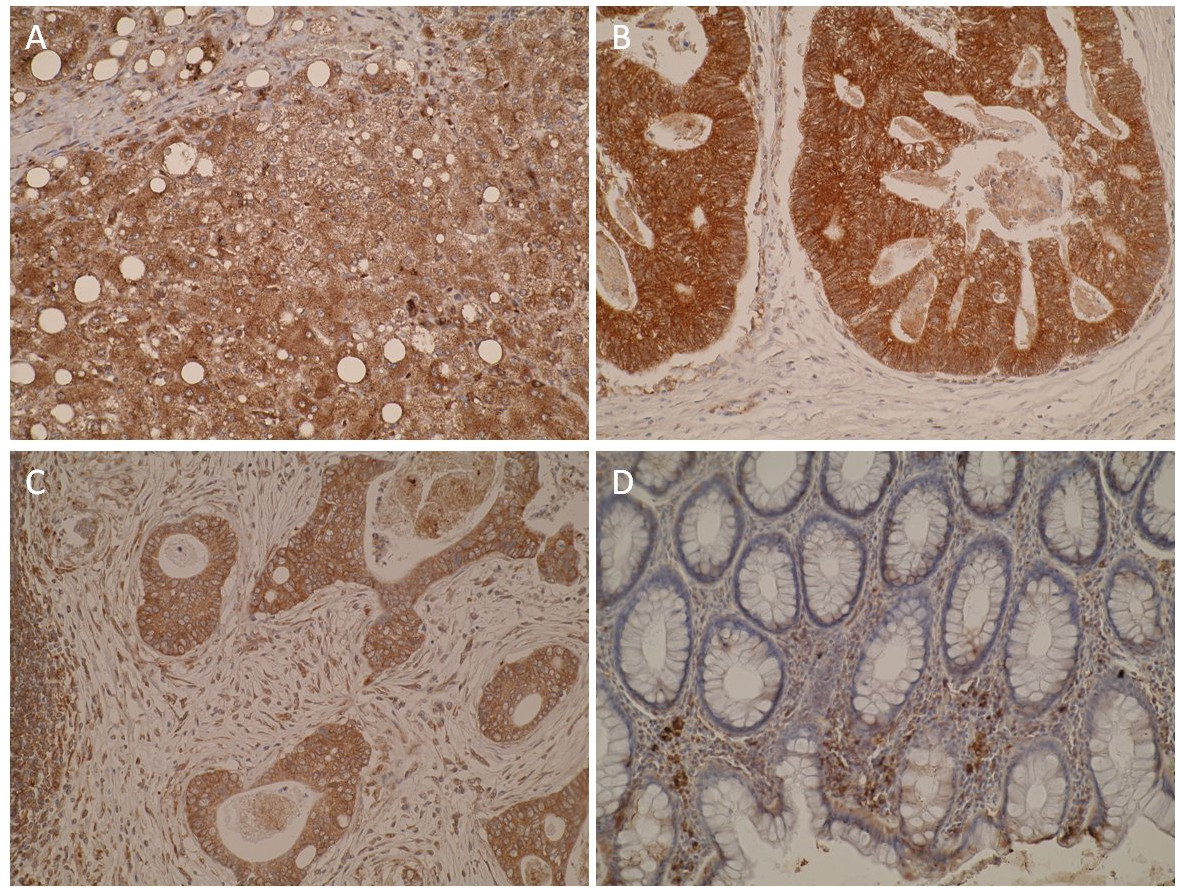
- Recommended controls: IHC: formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human liver sections WB: pooled human liver microsomes
Target Details
- Target: Cytochrome P450, family 7, subfamily B, polypeptide 1 (CYP7B1)
- Tissue cell line specificity: IHC: formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human liver sections WB: pooled human liver microsomes
- Target background: Defects in CYP7B1 are the cause of spastic paraplegia autosomal recessive type 5A (SPG5A) [MIM:270800]. Spastic paraplegia is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a slow, gradual, progressive weakness and spasticity of the lower limbs. Rate of progression and the severity of symptoms are quite variable. Initial symptoms may include difficulty with balance, weakness and stiffness in the legs, muscle spasms, and dragging the toes when walking. In some forms of the disorder, bladder symptoms (such as incontinence) may appear, or the weakness and stiffness may spread to other parts of the body. Defects in CYP7B1 are the cause of congenital bile acid synthesis defect type 3 (CBAS3) [MIM:613812]. Clinical features include severe cholestasis, cirrhosis and liver synthetic failure. Hepatic microsomal oxysterol 7-alpha-hydroxylase activity is undetectable.
Applications
- Application: ELISA ; IHC ; WB
Handling
- Format: Liquid
- Concentration: 1 mg/ml
- Unit size: 100 ug
- Storage buffer: PBS with 0.02% azide
- Storage conditions: -15° C to -25° C
- Shipping conditions: Dry ice
References
- Characterisation of the oxysterol metabolising enzyme pathway in mismatch repair proficient and deficient colorectal cancer.
- Swan et al. 2016. Oncotarget. :. PMID: 27341022.