Cat. #151203
Anti-CD33 [6C5/2]
Cat. #: 151203
Sub-type: Primary antibody
Unit size: 100 ug
Availability: 1-2 weeks
Target: SIGLEC3 (CD33)
Class: Monoclonal
Application: ELISA ; FACS ; IHC
Reactivity: Human
Host: Mouse
£300.00
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Inventor: Paul Crocker
Institute: University of Oxford
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
- Name: Anti-CD33 [6C5/2]
- Alternate name: Sialic Acid Binding Ig Like Lectin 12; SIGLECL1; SLG 3; Siglec-12; Siglec-L1; S2V
- Clone: CD33 6C5/2
- Tool sub type: Primary antibody
- Class: Monoclonal
- Conjugation: Unconjugated
- Reactivity: Human
- Host: Mouse
- Application: ELISA ; FACS ; IHC
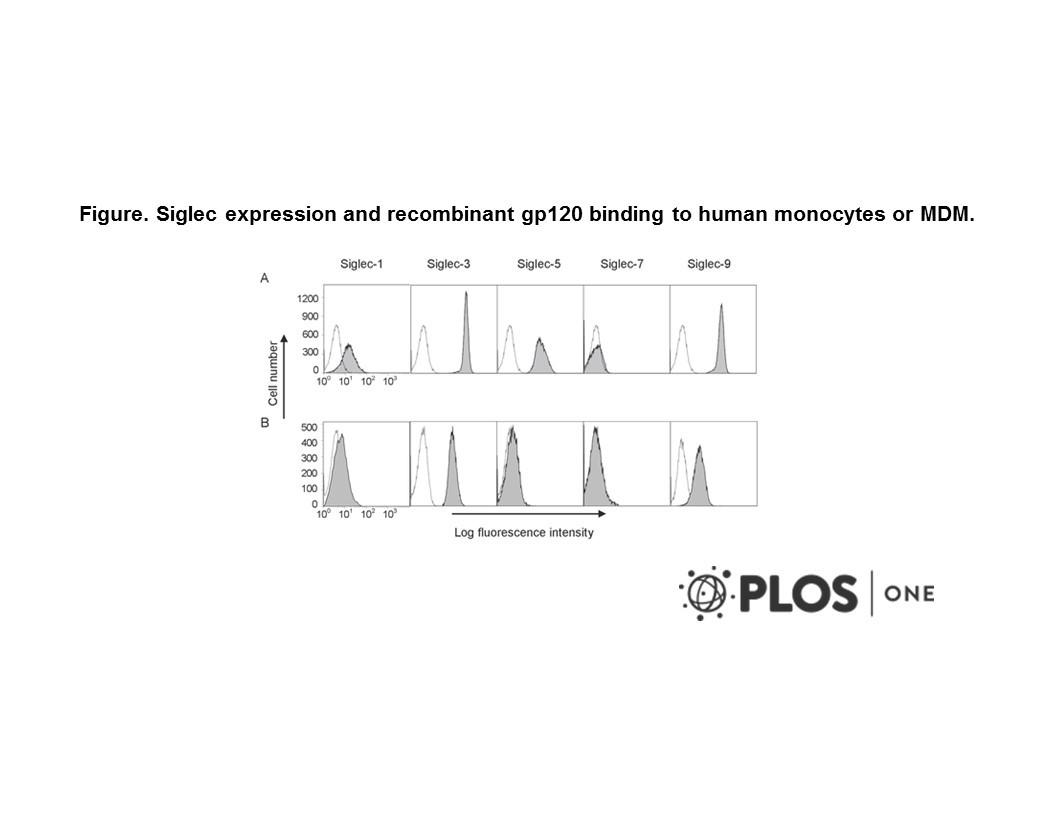
- Description: The SIGLECs are a family of membrane bound lectins (of the immunoglobulin superfamily) that bind sialic acid and mediate cell-cell interactions. Family members include sialoadhesin, CD22 and CD33. CD33 is found on granulocyte and macrophage precursors in the bone marrow, but not on pluripotent stem cells. CD33 is also expressed on, and a useful marker for, peripheral monocytes. CD33 is also useful for distinguishing myelogenous leukaemia cells from lymphoid or erythroid leukaemias. CD33 is a putative adhesion molecule of myelomonocytic-derived cells that mediates sialic-acid dependent binding to cells & preferentially binds to alpha-2,6-linked sialic acid. The sialic acid recognition site may be masked by cis interactions with sialic acids on the same cell surface. In the immune response, may act as an inhibitory receptor upon ligand induced tyrosine phosphorylation by recruiting cytoplasmic phosphatase(s) via their SH2 domain(s) that block signal transduction through dephosphorylation of signaling molecules. Induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia (in vitro).
- Immunogen: CD33-Fc recombinant protein
- Isotype: IgG1
- Myeloma used: Sp2/0-Ag14
- Recommended controls: CD33 transfected COS cells
Target Details
- Target: SIGLEC3 (CD33)
- Tissue cell line specificity: CD33 transfected COS cells
- Target background: The SIGLECs are a family of membrane bound lectins (of the immunoglobulin superfamily) that bind sialic acid and mediate cell-cell interactions. Family members include sialoadhesin, CD22 and CD33. CD33 is found on granulocyte and macrophage precursors in the bone marrow, but not on pluripotent stem cells. CD33 is also expressed on, and a useful marker for, peripheral monocytes. CD33 is also useful for distinguishing myelogenous leukaemia cells from lymphoid or erythroid leukaemias. CD33 is a putative adhesion molecule of myelomonocytic-derived cells that mediates sialic-acid dependent binding to cells & preferentially binds to alpha-2,6-linked sialic acid. The sialic acid recognition site may be masked by cis interactions with sialic acids on the same cell surface. In the immune response, may act as an inhibitory receptor upon ligand induced tyrosine phosphorylation by recruiting cytoplasmic phosphatase(s) via their SH2 domain(s) that block signal transduction through dephosphorylation of signaling molecules. Induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia (in vitro).
Applications
- Application: ELISA ; FACS ; IHC
Handling
- Format: Liquid
- Concentration: 1 mg/ml
- Unit size: 100 ug
- Storage buffer: PBS with 0.02% azide
- Storage conditions: -15° C to -25° C
- Shipping conditions: Shipping at 4° C
References
- Souza et al. 2019. Short-Term High-Fat Diet Consumption Reduces Hypothalamic Expression of the Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor a7 Subunit (a7nAChR) and Affects the Anti-inflammatory Response in a Mouse Model of Sepsis Front Immunol. 10:565. PMID: 309678
- Siglecs facilitate HIV-1 infection of macrophages through adhesion with viral sialic acids.
- The myeloid-specific sialic acid-binding receptor, CD33, associates with the protein-tyrosine phosphatases, SHP-1 and SHP-2.
- Characterization of CD33 as a new member of the sialoadhesin family of cellular interaction molecules.