Cat. #161587
Plasmax™, Glucose-Free Cell Culture Medium
Cat. #: 161587
Sub-type: Cell culture media
Unit size: 500 ml
Availability: 1-2 weeks
Application: Cell culture; Cell growth and viability; Glucose starvation experiments; Cancer metabolism studies; Metabolic flux analysis
Volume: 500 ml
£120.00
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Inventor: Saverio Tardito
Institute: CRUK Scotland Institute
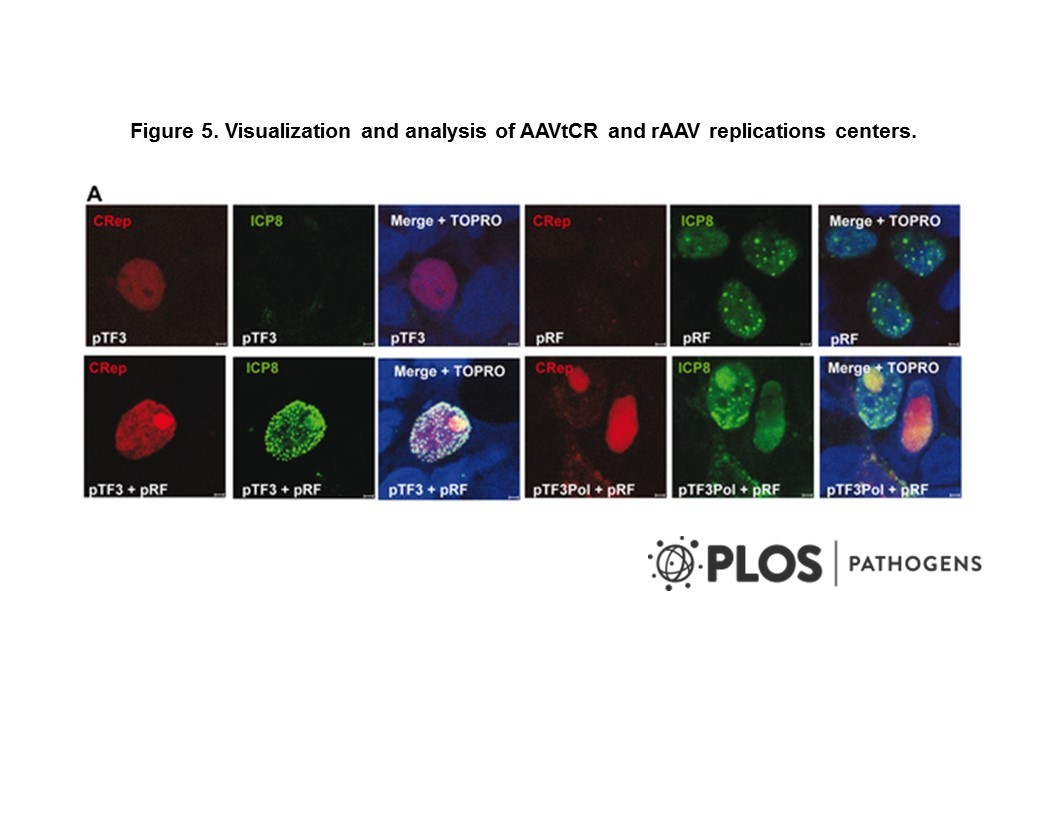
Primary Citation: Vande Voorde et al. 2019. Sci Adv. 5(1):eaau7314. PMID: 30613774
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY (for other uses, please contact the licensing team)
- Tool name: Plasmax™, Glucose-Free Cell Culture Medium
- Alternate name: Customised PlasmaxTM
- Research fields: Cancer;Cell biology
- Tool sub type: Cell culture media
- Purpose: A tailored cell culture solution based on physiologically relevant cell culture medium which mimics the metabolic and physiological profile of human plasma
- Formulation: PlasmaxTM cell culture media (Cat.# 156371) formulation without glucose. The PlasmaxTM cell culture media (Cat.# 156371) formulation can be found here.
- Application: Cell culture; Cell growth and viability; Glucose starvation experiments; Cancer metabolism studies; Metabolic flux analysis
Handling
- Format: Liquid
- Volume: 500 ml
- Storage conditions: Stable until expiry date on label
Application Details
- Application: Cell culture; Cell growth and viability; Glucose starvation experiments; Cancer metabolism studies; Metabolic flux analysis
- Application notes: The customised version of PlasmaxTM is created to fit your experiment’s unique requirements
Related Tools
- Related tools: 156371
References
- Bagshawet al. Mitochondrial Intoxication. 2023, 723-744
- Gassl et al. Cancers (Basel) 2022 Nov 16,14(22):5617. PMID: 36428711
- Wang et al. Biomolecules 2022 Oct 27,12(11):1575. PMID: 36358924
- Villar et al. 2022. Nat Chem Biol. PMID: 36280791
- Gardner et al. 2022. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 323(3):C823-C834. PMID: 35876286
- Golikov et al. 2022. Mol Biol (Mosk) 56(5):687-696. PMID: 36165010
- Taurino et al. 2022. Mol Metab. 101532 PMID: 35752287
- Wang et al. 2022. Biomolecules. 12(6):743. PMID: 35740868
- Bagshaw et al. 2021. Biomaterials and Biosystems.4 (100027): 2666-5344
- Golikov et al. 2022. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 97.
- Golikov et al. Antioxidants 2022, 11(1), 97
- Kalimuthu et al. 2021. J Cell Biochem. :. PMID: 34935169.
- Hennequart et al. 2021. Nature Communications. 12: 6176.
- Chiu et al. 2021. American Society of Hematology. Blood Advances.
- Cox et al. 2020. Journal of Data and Information Science. 5(3): 161-177
- Moradi et al. 2021. Biomolecules. 11(8): 1177
- Plasmax Application Note
- Barekatain et al. 2021. Nature. 12: 4228.
- Moradi et al. 2021. American Journal of Physiology. Cell Physiology. 321 (1): C72-C81.
- Khadka et al. 2021. Cancer & Metabolism. 9:27
- Abbas et al. 2021. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 254:110570. PMID: 33516822.
- PlasmaxTM: Product Brochure
- Ackermann et al. 2019. Trends Cancer. 5(6):329-332. PMID: 31208694.
- Cell culture shock – a scientist’s hunt for the perfect cocktail
- Vande Voorde et al. 2019. Sci Adv. 5(1):eaau7314. PMID: 30613774.


![Anti-CAR Whitlow Linker [1C3C3]](https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-6-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025-300x322.jpg 300w, https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-6-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025-280x300.jpg 280w, https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-6-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025-954x1024.jpg 954w, https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-6-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025-768x824.jpg 768w, https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-6-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025.jpg 1193w)

![Anti-CAR Whitlow Linker [1B4A1]](https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-5-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025-300x396.jpg 300w, https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-5-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025-227x300.jpg 227w, https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-5-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025-776x1024.jpg 776w, https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-5-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025-768x1013.jpg 768w, https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-5-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025.jpg 970w)