Cat. #154474
Glycated HSA Rhodamine Boronic Acid small molecule (tool compound)
Cat. #: 154474
Availability: Please enquire for quantities and pricing
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Inventor: Marta P. Pereira Morais
Institute: University of Bath
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY (for other uses, please contact the licensing team)
- Tool name: Glycated HSA Rhodamine Boronic Acid small molecule (tool compound)
- Alternate name: AGEs
- Research fields: Cancer;Cell biology
- Primary target: Advanced Glycation Endproducts (AGE); specifically Glycated Human Serum Albumin (HSA). Also binds ApoA-I protein.
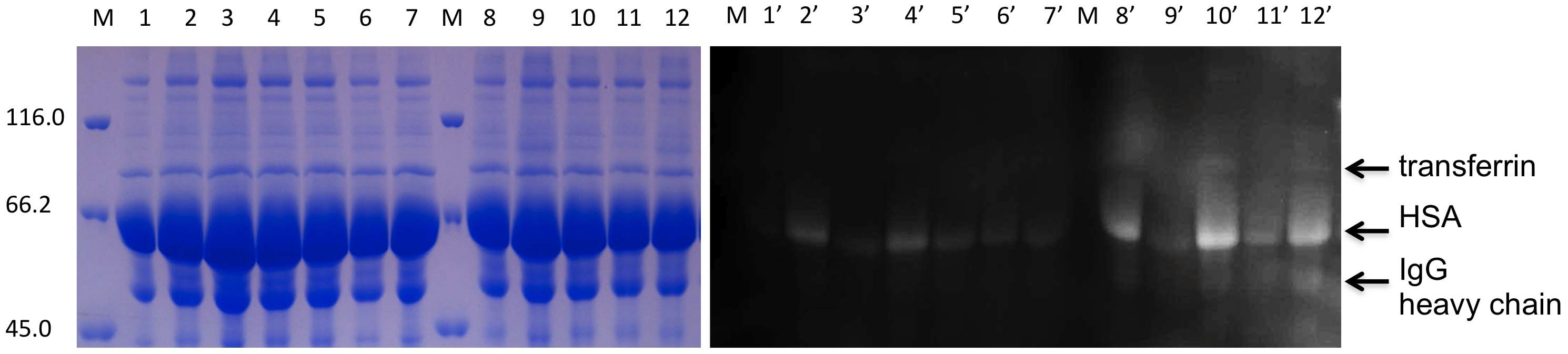
- Description: Protein glycation, also known as non-enzymatic glycosylation, has been implicated in various disease states and is therefore an important biomarker for ageing and age-related chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune diseases, cancer, and Alzheimer's disease. However their analysis is challenging due to the complexity of the protein-carbohydrate adducts. Fluorescent boronic acids like these enable the detection and identification of individual glycated proteins in...
- Additional notes: This small molecule has been used to identify glycated proteins in human serum, insect hemolymph, and mouse brain homogenates.
Handling
- Shipping conditions: Dry Ice
Target Details
- Primary target: Advanced Glycation Endproducts (AGE); specifically Glycated Human Serum Albumin (HSA). Also binds ApoA-I protein.
References
- Pereira Morais et al. 2013. Sci Rep. 3:1437. PMID: 23531746.


![Anti-CAR Whitlow Linker [1C3C3]](https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-6-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025-300x322.jpg 300w, https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-6-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025-280x300.jpg 280w, https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-6-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025-954x1024.jpg 954w, https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-6-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025-768x824.jpg 768w, https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/Figure-6-Kimble-et-al.-J-Immunother-Cancer-2025.jpg 1193w)

