Cat. #151718
Prox1CreERT2 Mouse
Cat. #: 151718
Sub-type: Mouse
Availability: 6-8 weeks
Model: Conditional KO
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Inventor: Taija Makinen
Institute: Cancer Research UK, London Research Institute: Lincoln's Inn Fields
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
- Tool name: Prox1CreERT2 Mouse
- Tool sub type: Mouse
- Model: Conditional KO
- Conditional: Yes
- Conditional description: Cre-ER transgenic
- Description: Allows specific and temporally controlled cre-loxP recombination (gene inactivation/activation) in Prox1-expressing tissues, including lymphatic endothelia. Efficient recombination is observed during all developmental stages (embryonic, postnatal) and in adults. Currently no other models are available that allow such efficient and specific targetting of lymphatic vasculature. Transgenic mouse expressing tamoxifen-inducible creERT2 under the control of Prox1 gene promoter
- Genetic background: A cDNA encoding tamoxifen inducible Cre recombinase (CreERT2) followed by SV40 polyadenylation signal was introduced into the start codon of Prox1 in BAC clone RP23-190F21 using homologous recombination in bacteria. The construct was validated by PCR and Southern blot analyses, and used for pronuclear injection into fertilised mouse oocytes. Two founder lines were generated and tested by timed matings with Cre reporter strains, followed by 4-OHT administration, for specificity and efficiency of Cre-mediated recombination. One of the founder lines that gave efficient recombination in all Prox1-expressing tissues was kept for further studies.
- Zygosity: Heterozygous
- Production details: A cDNA encoding tamoxifen inducible Cre recombinase (CreERT2) followed by SV40 polyadenylation signal was introduced into the start codon of Prox1 in BAC clone RP23-190F21 using homologous recombination in bacteria. The construct was validated by PCR and Southern blot analyses, and used for pronuclear injection into fertilised mouse oocytes. Two founder lines were generated and tested by timed matings with Cre reporter strains, followed by 4-OHT administration, for specificity and efficiency of Cre-mediated recombination. One of the founder lines that gave efficient recombination in all Prox1-expressing tissues was kept for further studies.
Handling
- Shipping conditions: Embryo/Spermatoza- Dry Ice
Target Details
- Target: Prox1
References
- Bianchi et al. 2015. PLoS One. 10(4):e0122976. PMID: 25849579.
- Martinez-Corral et al. 2015. Circ Res. 116(10):1649-54. PMID: 25737499.
- Rouhani et al. 2015. Nat Commun. 6:6771. PMID: 25857745.
- Roles of lymphatic endothelial cells expressing peripheral tissue antigens in CD4 T-cell tolerance induction.
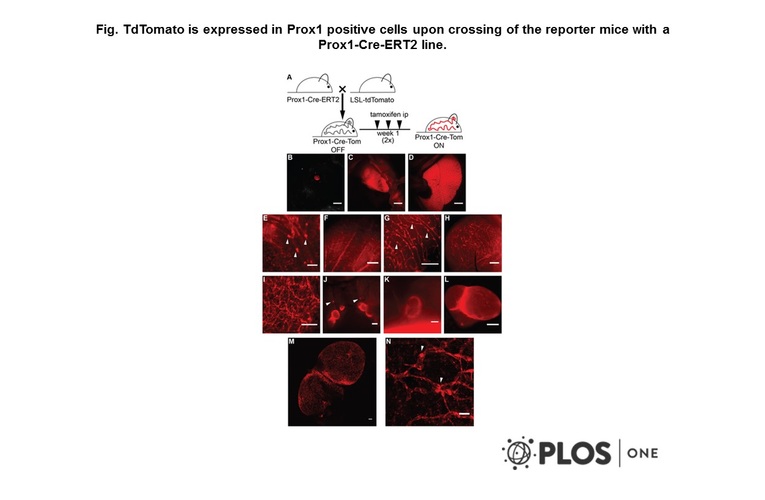
- A transgenic Prox1-Cre-tdTomato reporter mouse for lymphatic vessel research.
- Nonvenous origin of dermal lymphatic vasculature.
- Park et al. 2014. J Clin Invest. 124(9):3960-74. PMID: 25061877.
- Aspelund et al. 2014. J Clin Invest. 124(9):3975-86. PMID: 25061878.
- The Schlemm's canal is a VEGF-C/VEGFR-3-responsive lymphatic-like vessel.
- Lymphatic regulator PROX1 determines Schlemm's canal integrity and identity.
- Tatin et al. 2013. Dev Cell. 26(1):31-44. PMID: 23792146.
- Planar cell polarity protein Celsr1 regulates endothelial adherens junctions and directed cell rearrangements during valve morphogenesis.
- Chen et al. 2012. J Clin Invest. 122(6):2006-17. PMID: 22622036.
- Blood flow reprograms lymphatic vessels to blood vessels.
- Sabine et al. 2012. Dev Cell. 22(2):430-45. PMID: 22306086.
- Mechanotransduction, PROX1, and FOXC2 cooperate to control connexin37 and calcineurin during lymphatic-valve formation.
- Bazigou et al. 2011. J Clin Invest. 121(8):2984-92. PMID: 21765212.
- Genes regulating lymphangiogenesis control venous valve formation and maintenance in mice.