Cat. #153651
Anti-Growth Differentiation Factor 9 [53/1]
Cat. #: 153651
Sub-type: Primary antibody
Unit size: 100 ug
Availability: 10-12 weeks
Target: Growth Differentiation Factor 9
Class: Monoclonal
Application: ELISA ; IHC ; WB
Reactivity: Human
Host: Mouse
£300.00
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Institute: BioServ UK Ltd
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY (for other uses, please contact the licensing team)
- Name: Anti-Growth Differentiation Factor 9 [53/1]
- Alternate name: Growth/differentiation factor 9, GDF-9, GDF9
- Research fields: Cell signaling and signal transduction
- Clone: 53/1
- Tool sub type: Primary antibody
- Class: Monoclonal
- Conjugation: Unconjugated
- Molecular weight: 17.5 kDa
- Strain: Balb/c
- Reactivity: Human
- Host: Mouse
- Application: ELISA ; IHC ; WB
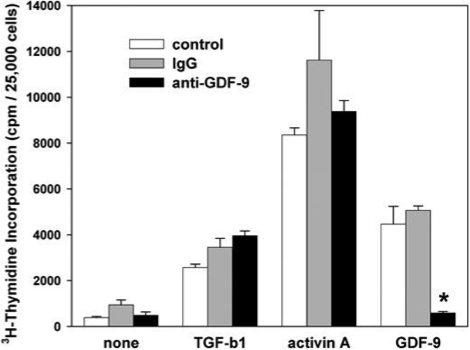
- Description: GDF9 is plays a vital role in ovarian folliculogenesis, follicle development and fertility. Clone 53/1 can be used in assays to detect oocyte expression and has been shown to neutralize GDF9 biological activity.
- Immunogen: Tuberculin coupled peptide with sequence VPAKYSPLSVLTIEPDGSIAYKEYEDMIATKC that recognizes an epitope with the EPDG sequence near the C-terminal region of human GDF9
- Isotype: IgG1
- Myeloma used: Sp2/0-Ag14
- Recommended controls: Ovary
Target Details
- Target: Growth Differentiation Factor 9
- Molecular weight: 17.5 kDa
- Tissue cell line specificity: Ovary
- Target background: GDF9 is plays a vital role in ovarian folliculogenesis, follicle development and fertility. Clone 53/1 can be used in assays to detect oocyte expression and has been shown to neutralize GDF9 biological activity.
Applications
- Application: ELISA ; IHC ; WB
Handling
- Format: Liquid
- Unit size: 100 ug
- Shipping conditions: Dry ice
References
- Li et al. 2015. Mol Endocrinol. 29(1):40-52. PMID: 25394262.
- Modifications of human growth differentiation factor 9 to improve the generation of embryos from low competence oocytes.
- Simpson et al. 2014. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 99(4):E615-24. PMID: 24438375.
- Aberrant GDF9 expression and activation are associated with common human ovarian disorders.
- Simpson et al. 2012. Endocrinology. 153(3):1301-10. PMID: 22234469.
- Activation of latent human GDF9 by a single residue change (Gly 391 Arg) in the mature domain.
- Mottershead et al. 2008. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 283(1-2):58-67. PMID: 18162287.
- Characterization of recombinant human growth differentiation factor-9 signaling in ovarian granulosa cells.
- Gilchrist et al. 2004. Biol Reprod. 71(3):732-9. PMID: 15128595.
- Immunoneutralization of growth differentiation factor 9 reveals it partially accounts for mouse oocyte mitogenic activity.

![Anti-Growth Differentiation Factor 9 [53/1] - Image 2](https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/88075484-2441-4215-96f0-44e737151076.png)
![Anti-Growth Differentiation Factor 9 [53/1] - Image 3](https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/a5526a10-761a-4810-9c1c-3c968f3c03fe.png)
![Anti-Growth Differentiation Factor 9 [53/1] - Image 4](https://cancertools.org/wp-content/uploads/ad5748ec-5886-4a14-a196-4f8dc4268cc3.png)

